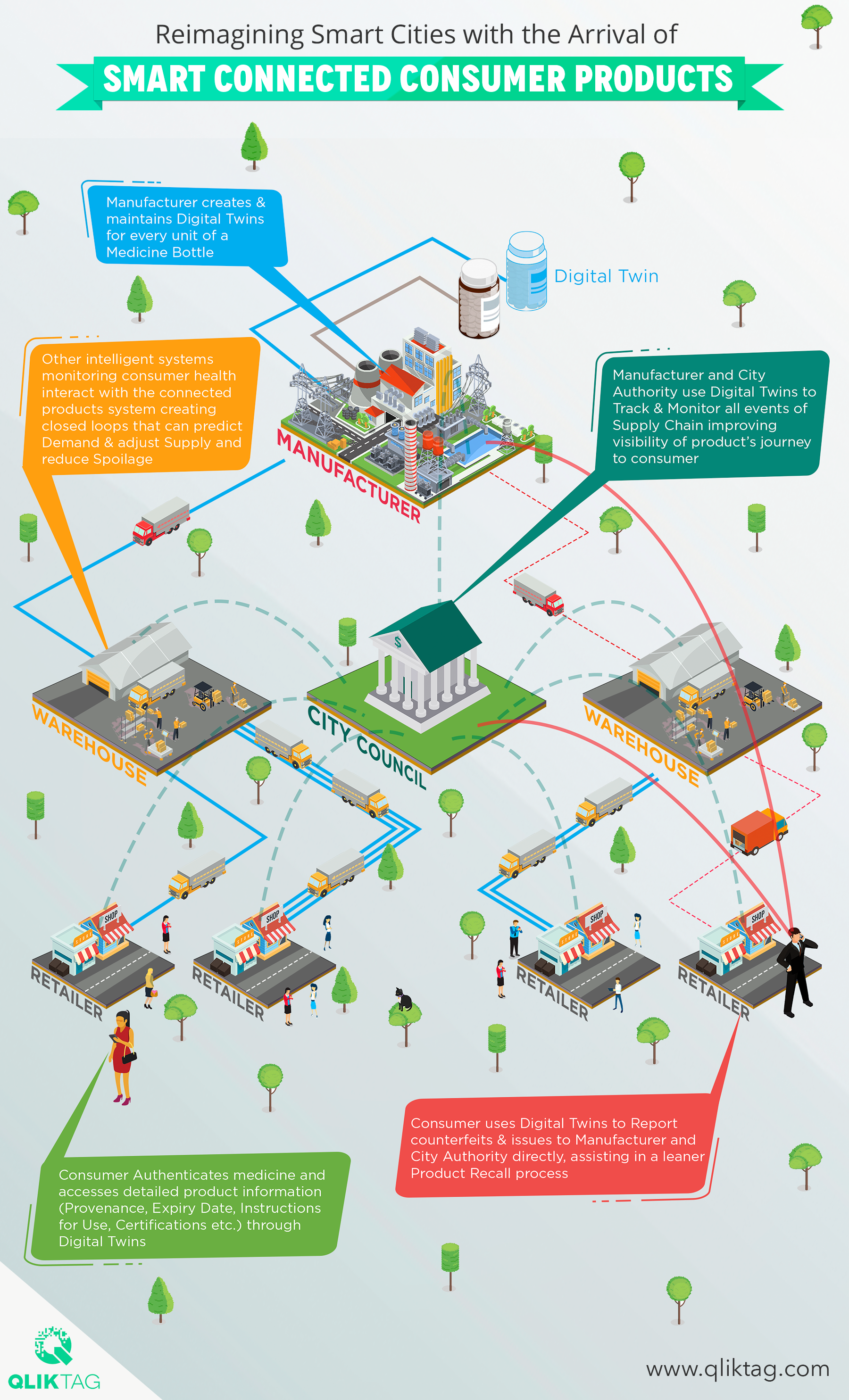
The Dawn of the Intelligent City
For centuries, cities have been centers of innovation, commerce, and culture. However, rapid urbanization presents unprecedented challenges – from traffic congestion and pollution to resource management and public safety. Traditional urban planning approaches are often reactive, struggling to keep pace with the dynamic needs of a growing population. The solution lies in embracing intelligent systems, leveraging data and technology to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable urban environments. This isn't simply about implementing 'smart' gadgets; it's a fundamental reimagining of how cities function, prioritizing citizen well-being and long-term resilience.
The core principle behind intelligent cities is the interconnectedness of systems. Sensors embedded throughout the urban landscape collect real-time data on everything from air quality and traffic flow to energy consumption and waste levels. This data is then analyzed using advanced algorithms – including artificial intelligence and machine learning – to identify patterns, predict trends, and optimize resource allocation. The result is a city that responds proactively to the needs of its inhabitants, rather than reacting to problems after they arise.
Transforming Urban Mobility with Data
One of the most visible impacts of intelligent systems is in the realm of urban mobility. Traditional traffic management relies on fixed timing plans, often leading to congestion and delays. Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) utilize real-time data from sensors, cameras, and even mobile devices to dynamically adjust traffic signals, optimize routes, and provide drivers with up-to-the-minute information about road conditions. This not only reduces commute times but also lowers fuel consumption and emissions.
Beyond optimizing existing infrastructure, intelligent systems are paving the way for new modes of transportation. Ride-sharing services, autonomous vehicles, and smart parking solutions are all powered by data and algorithms, offering citizens more convenient and sustainable transportation options. Furthermore, integrated public transportation systems, providing seamless connections between buses, trains, and other modes, are becoming increasingly common, encouraging a shift away from private car ownership.
Predictive analytics play a crucial role here. By analyzing historical traffic patterns and current conditions, systems can anticipate congestion hotspots and proactively reroute traffic, preventing bottlenecks before they even form. This level of foresight is simply impossible with traditional methods.
Sustainable Resource Management and Enhanced Public Safety
The benefits of intelligent systems extend far beyond transportation. Smart grids, powered by sensors and data analytics, optimize energy distribution, reduce waste, and integrate renewable energy sources more effectively. Similarly, smart water management systems detect leaks, monitor water quality, and optimize water usage, conserving this precious resource. Waste management is also being revolutionized, with sensors in bins monitoring fill levels and optimizing collection routes, reducing costs and environmental impact.
Public safety is another area where intelligent systems are making a significant difference. Predictive policing algorithms analyze crime data to identify areas at high risk of criminal activity, allowing law enforcement to deploy resources more effectively. Smart surveillance systems, equipped with facial recognition and anomaly detection capabilities, can enhance security and respond quickly to emergencies. However, it’s vital to address ethical concerns surrounding data privacy and potential biases in these systems.
The integration of these systems creates a synergistic effect. For example, data from smart lighting systems can be used to improve public safety, while data from environmental sensors can be used to optimize energy consumption. This holistic approach is essential for creating truly intelligent and sustainable cities.
Key Components of an Intelligent City Ecosystem
- Sensor Networks: The foundation of data collection, providing real-time information on various urban parameters.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Processing and analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by sensor networks.
- Communication Infrastructure: Reliable and secure communication networks (e.g., 5G) to transmit data between devices and systems.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: Algorithms that identify patterns, predict trends, and automate decision-making.
- Citizen Engagement Platforms: Tools that allow citizens to provide feedback, report issues, and participate in urban planning.
