Introduction to Low-Code/No-Code Development
Low-code and no-code development platforms are rapidly changing the landscape of software creation. Traditionally, building applications required extensive coding knowledge and a significant investment in developer resources. These new platforms empower a wider range of individuals – including citizen developers, business analysts, and IT professionals – to create applications with minimal or no hand-coding. This shift is driven by the increasing demand for digital solutions and the need for faster time-to-market.
The core principle behind these platforms is visual development. Instead of writing lines of code, users interact with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and drag-and-drop components to assemble applications. This approach significantly reduces the complexity and time associated with traditional development methods, allowing organizations to respond more quickly to changing business needs.
Understanding the Differences: Low-Code vs. No-Code
While often used interchangeably, low-code and no-code platforms differ in their approach to coding. No-code platforms are designed for users with absolutely no programming experience. They typically offer pre-built templates and components that can be configured to create simple applications, such as basic websites, forms, or workflows. The focus is on ease of use and rapid prototyping.
Low-code platforms, on the other hand, allow some level of coding customization. They provide visual development tools but also enable developers to add custom code when necessary to address more complex requirements. This flexibility makes low-code platforms suitable for building more sophisticated applications that require integration with existing systems or specialized functionality. They bridge the gap between the simplicity of no-code and the power of traditional coding.
Essentially, no-code is about configuration, while low-code is about configuration *and* extension. Both aim to accelerate development, but they cater to different skill sets and application complexities.
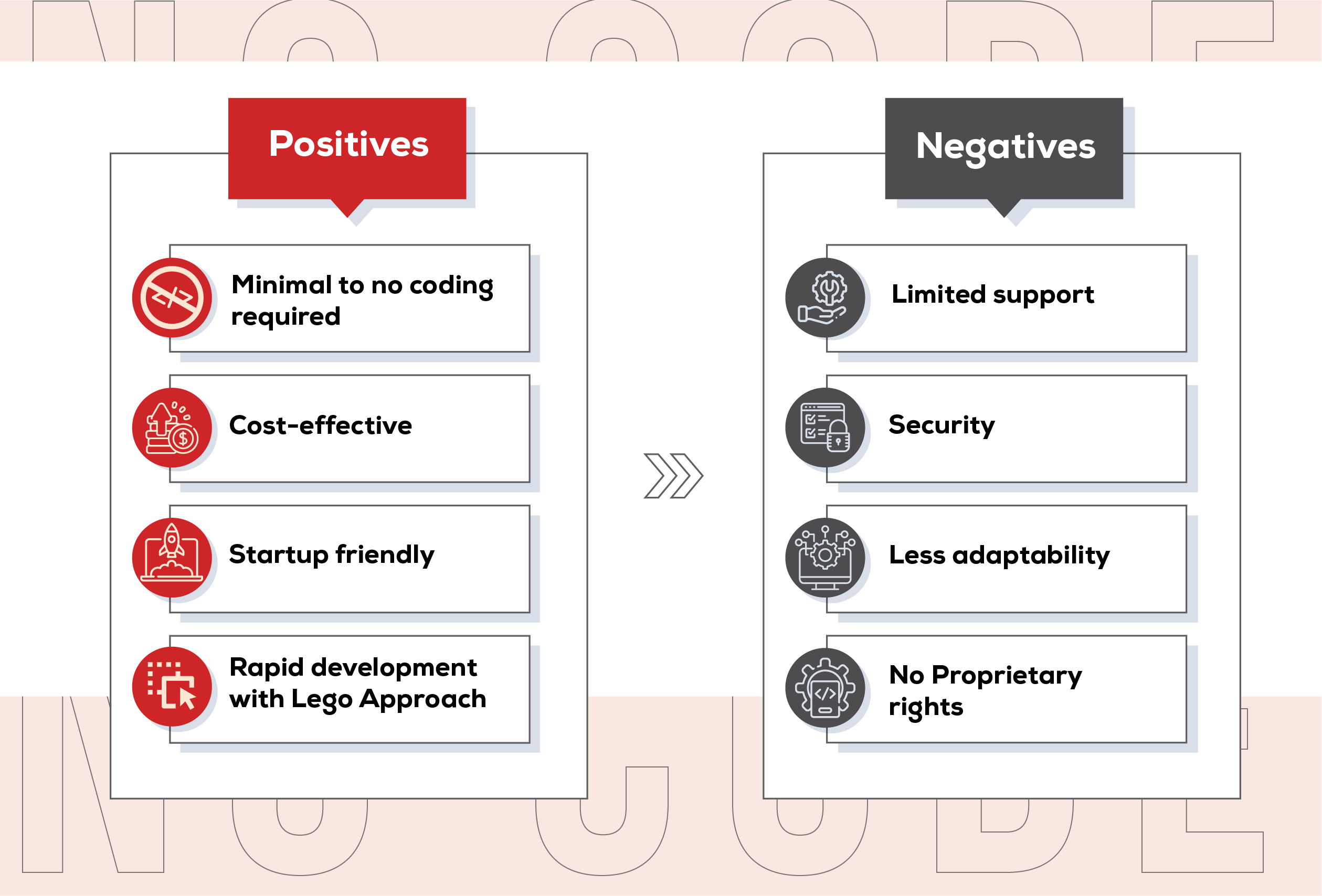
Benefits and Use Cases
The advantages of adopting low-code/no-code development are numerous. Reduced development costs are a primary benefit, as fewer developers are needed. Faster time-to-market is another key advantage, allowing organizations to deploy applications more quickly and gain a competitive edge. Furthermore, these platforms often promote increased agility, enabling businesses to adapt to changing requirements more easily.
The use cases for low-code/no-code are incredibly diverse. They are particularly well-suited for automating business processes, building customer relationship management (CRM) systems, creating mobile applications, and developing internal tools. They can also be used to rapidly prototype new ideas and validate concepts before investing in full-scale development.
Here are some common applications:
- Workflow Automation: Streamlining repetitive tasks and processes.
- Mobile App Development: Creating mobile applications for internal or external use.
- Web Application Development: Building web-based applications for various purposes.
- Data Collection & Forms: Designing and deploying online forms for data gathering.
- Process Improvement: Digitizing and optimizing existing business processes.
