Delving into the Dark Web: What It Is and How It Works
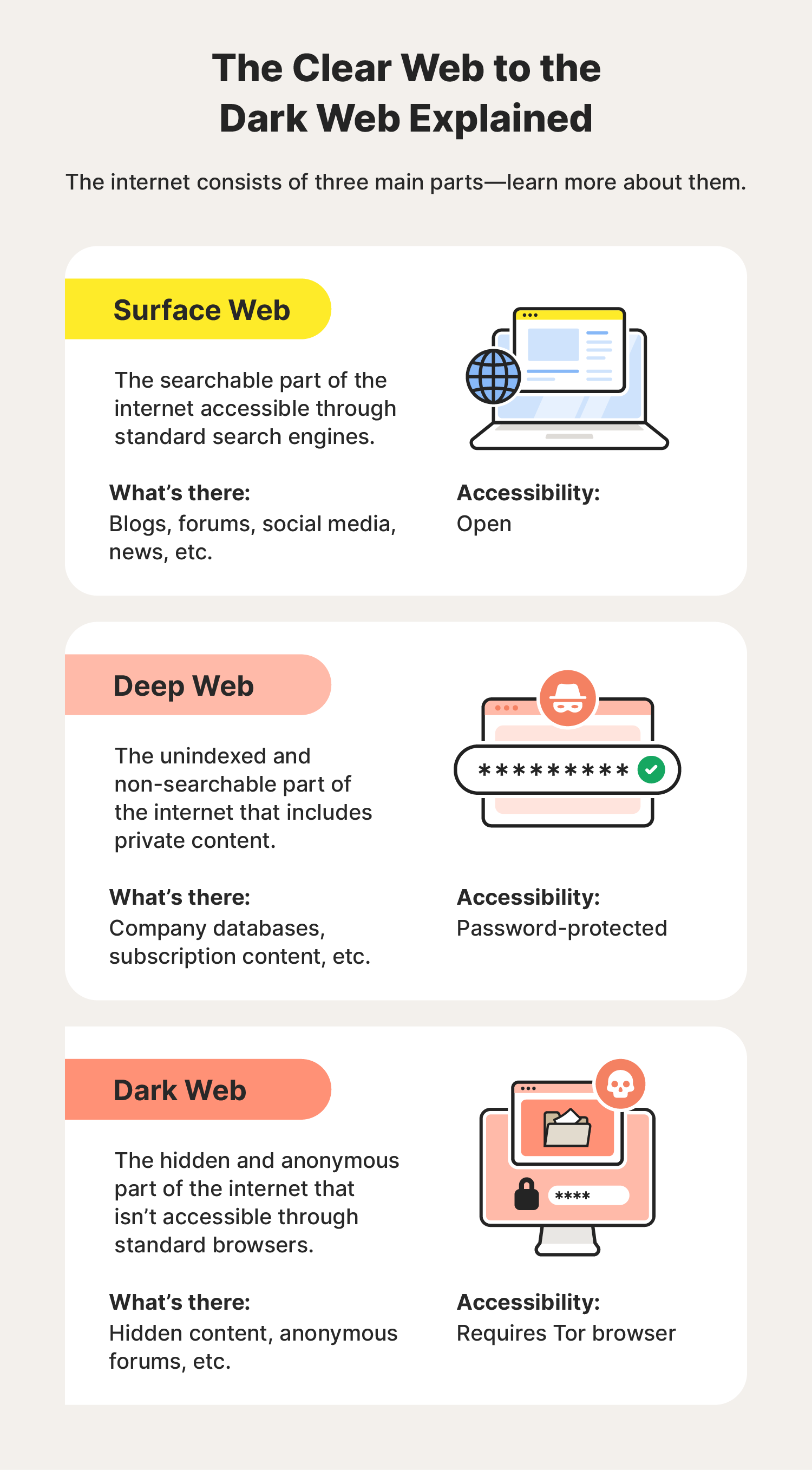
The internet as we know it – the surface web – is just the tip of the iceberg. Beneath it lie layers of the deep web and, most notably, the dark web. Often shrouded in mystery and associated with illicit activities, the dark web is a complex and often misunderstood part of the digital world. This article aims to demystify the dark web, explaining what it is, how it works, and the risks associated with accessing it.
What is the Dark Web?
The dark web is a small portion of the deep web, which refers to content not indexed by standard search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. This includes things like online banking portals, email inboxes, and content behind paywalls. The dark web, however, is intentionally hidden and requires specific software, configurations, or authorization to access.
Unlike the surface web, which uses standard internet protocols, the dark web relies on anonymizing networks like Tor (The Onion Router) and I2P (Invisible Internet Project). These networks encrypt and route internet traffic through a series of relays, making it extremely difficult to trace back to the user’s original IP address.
How Does the Dark Web Work?
The core technology enabling the dark web is onion routing. Here’s a simplified explanation:
- Encryption: When you access the dark web, your data is encrypted in multiple layers, like the layers of an onion.
- Relays: This encrypted data is then passed through a series of randomly selected relays (nodes) operated by volunteers around the world.
- Decryption: Each relay decrypts only one layer of encryption, revealing only the next destination relay.
- Anonymity: This process makes it virtually impossible to trace the origin and destination of the data.
Dark web addresses don't end in familiar extensions like .com or .org. Instead, they typically use the ".onion" pseudo-top-level domain, which is only accessible through the Tor browser.
What Can You Find on the Dark Web?
The dark web hosts a wide range of content, both legal and illegal. Here's a breakdown:
| Legal Uses | Illegal Uses |
|---|---|
| Privacy-focused communication | Illegal marketplaces (drugs, weapons, stolen data) |
| Whistleblowing platforms | Hacking services |
| Access to uncensored information | Distribution of illegal content (child exploitation material) |
| Secure file sharing | Financial fraud |
It’s crucial to understand that while the dark web can offer benefits for privacy and freedom of speech, it’s overwhelmingly associated with criminal activity.
Risks of Accessing the Dark Web
Accessing the dark web carries significant risks:
- Malware: Dark web sites are often poorly secured and can contain malware that can infect your device.
- Illegal Content: Accidentally stumbling upon illegal content can have legal consequences.
- Scams: Many dark web marketplaces are scams designed to steal your money or personal information.
- Surveillance: While Tor provides anonymity, it’s not foolproof. Law enforcement agencies actively monitor the dark web.
- Exposure to Disturbing Content: The dark web contains extremely disturbing and graphic content.
How to Access the Dark Web (and Why You Probably Shouldn't)
The most common way to access the dark web is through the Tor Browser. However, it's strongly advised against accessing the dark web unless you have a compelling reason and understand the risks involved. If you choose to do so, take the following precautions:
- Use a VPN in conjunction with Tor.
- Keep your software up to date.
- Disable JavaScript.
- Use a secure operating system.
- Never download files from untrusted sources.
Conclusion
The dark web is a fascinating but dangerous corner of the internet. While it offers potential benefits for privacy and freedom of expression, it’s primarily known for its association with illegal activities and the risks it poses to users. For most individuals, the risks far outweigh any potential benefits, and it’s best to avoid accessing it altogether.
